Thriving Farm: Corn

💡 Want more business insights? Stay ahead of the curve with our exclusive updates!
👉 Join our Telegram channel for daily business ideas and expert tips.
👉 Follow us on Facebook to never miss a trend or update!
Don’t just read—connect, grow, and innovate with us today!
Starting your own vegetable farm is a great business idea, especially considering the lack of government support for this sector, primarily in the form of subsidized loans and financing. Anyone can become a farmer from scratch. One of the most profitable crops to grow in the southern regions of Europe or America is corn. Experts estimate the profitability of this business to be around 400–800%. Ideal regions for corn cultivation include areas like Southern Spain, Italy, France, and parts of California. The Far East and the Pacific Northwest are also suitable for growing corn.
Economic Value of Corn

Corn, rich in carbohydrates, protein, and fats, is the basis for animal feed, with a value of 1.34 feed units per 1 kg of grain. This crop is essential for producing silage — a succulent feed for livestock. It is also used as green fodder.
Corn plays a significant role in starch production, used in both food and industrial applications. While edible in its raw form, corn cobs are preserved or processed to make flour and oil. By the way, producing vegetable oil is also a highly profitable business. Approximately one-fifth of the harvest is exported.
In agriculture and horticulture, corn is valued for its excellent agronomic qualities. Fields where corn was grown in the previous season are less prone to weed infestation. Moreover, this crop has few common pests that affect other valuable agricultural plants.
Corn Cultivation Conditions

Establishing a profitable corn business depends on meeting optimal growth conditions for this cereal crop.
- Temperature. Seed germination occurs at 8–9 degrees Celsius, with shoots emerging at 12–14 degrees (soil temperature at a depth of 10 cm). The plant's active growth phase is observed at temperatures between 24–28 degrees. Seedlings can withstand frost down to -3 degrees, with only the growth point remaining viable. High temperatures above 30 degrees harm the plant's generative organs, causing pollen and silk to dry out.
- Humidity. Corn is resistant to drought and sometimes requires reduced soil moisture for abundant fruiting. Compared to other vegetables, corn is less tolerant of excess moisture, which can disrupt nitrogen and phosphorus metabolism in cells. However, a lack of moisture during flowering and seed maturation negatively impacts the yield's quality and quantity.
- Light. Corn thrives when planted in open, well-lit areas. Its vegetative period increases with more than 12 hours of daylight. Dense planting can lead to excessive shading, resulting in reduced photosynthesis, especially detrimental when fodder corn is intended for silage production. Planting density on a one-hectare plantation ranges from 52 to 80 thousand adult plants, requiring 4–6.2 seeds per meter.
- Soil. Corn is not highly demanding but is sensitive to deficiencies in elements such as nitrogen, phosphorus, oxygen, and potassium. When grown in nutrient-poor soils, corn becomes less resistant to pests, grows slowly, and yields less. Optimal soil conditions are loamy soils or medium loamy soils, as well as loams.
Corn Farm: Financial Perspective
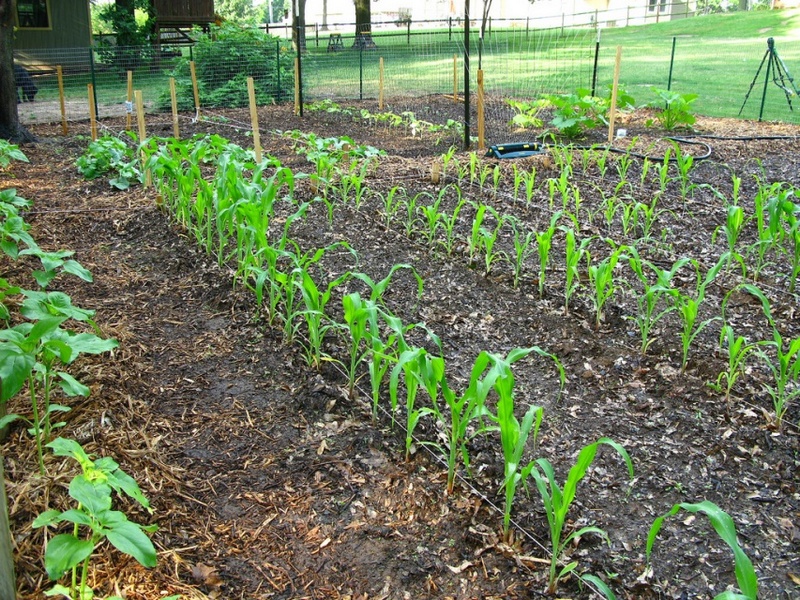

Setting up such a business requires land, seeds, equipment, and labor. Among these, land and machinery are the costliest, but both can be leased. Hiring employees with their own equipment, like a combine harvester, can help save costs.

Land rental prices are based on cadastral value, considering ecological factors and location in relation to regional infrastructure. In 2015, the average rental price for one hectare of land in Southern Europe or America was about 500 Euros, with future seasons expected to see an increase due to currency fluctuations. Another cost is pre-sowing soil preparation, which involves plowing the land. You can either rent equipment and plow the land yourself or hire a plowman with their tractor. On average, preparing one hectare costs about 200 Euros.
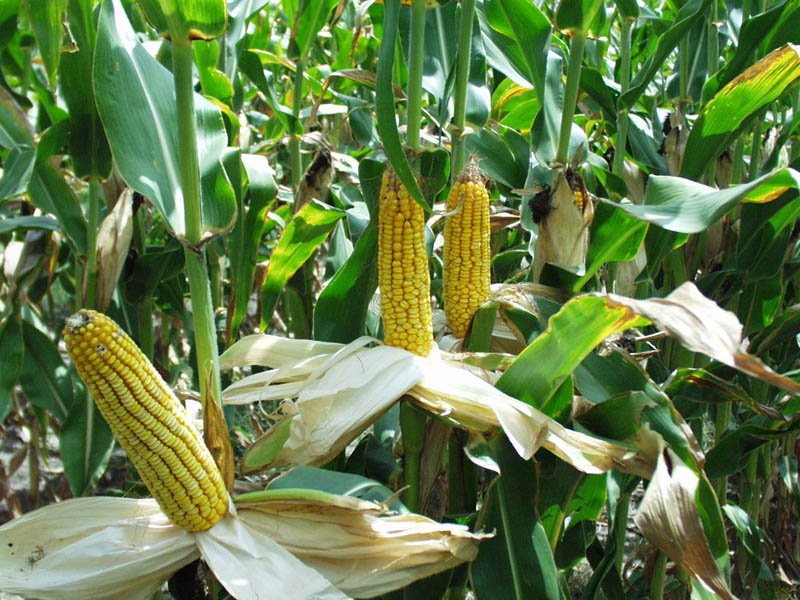

Seed costs vary depending on the supplier and hybrid variety, usually priced per seed, kilogram, or unit. On average, purchasing seeds for one hectare can cost around 30,000 Euros. The choice of hybrid variety depends on the desired market for the agricultural produce. For canning or cooking, F1 hybrids like Patoka, Spirit, and Super Sandance are optimal. Since the cost of a corn planter is relatively high, reaching 1.5 million Euros, leasing such equipment can lead to significant savings.
Corn cultivation requires expenditures for weed control, starting with harrowing and applying herbicides. Additional costs include maintenance operations (tillage, irrigation, fertilization) and harvesting. The total care costs depend on growing conditions but averaged around 55,000 Euros per hectare in 2016. Harvesting expenses vary based on the plantation size and plant density. Workers can harvest up to 2500 cobs per shift, with a payment of 500 Euros per shift.

If you are interested in farming ideas, don't forget to subscribe to our website's newsletter and share this article on social media. We also recently discussed how to open your own grocery store, which might also pique your interest.
💡 Want more business insights? Stay ahead of the curve with our exclusive updates!
👉 Join our Telegram channel for daily business ideas and expert tips.
👉 Follow us on Facebook to never miss a trend or update!
Don’t just read—connect, grow, and innovate with us today!





































.jpeg)













Note: Comments are being moderated and may take a while to appear. There is no need to resubmit your comment.